When you register a domain name, three key roles are involved: the Registry, the Registrar, and the Registrant. Understanding these roles helps clarify how domain names are managed on the internet.
Quick Analogy
Think of the domain name system like renting an apartment:
-
The Registry is the landlord who owns the building (the top-level domain, like .COM).
-
The Registrar is the real estate agent who helps you rent an apartment (register a domain).
-
The Registrant is you, the person renting and living in the apartment (owning the domain).
Who Oversees the System?
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) is the global organization that coordinates and accredits registries and registrars, ensuring the stability and security of the domain namesystem.
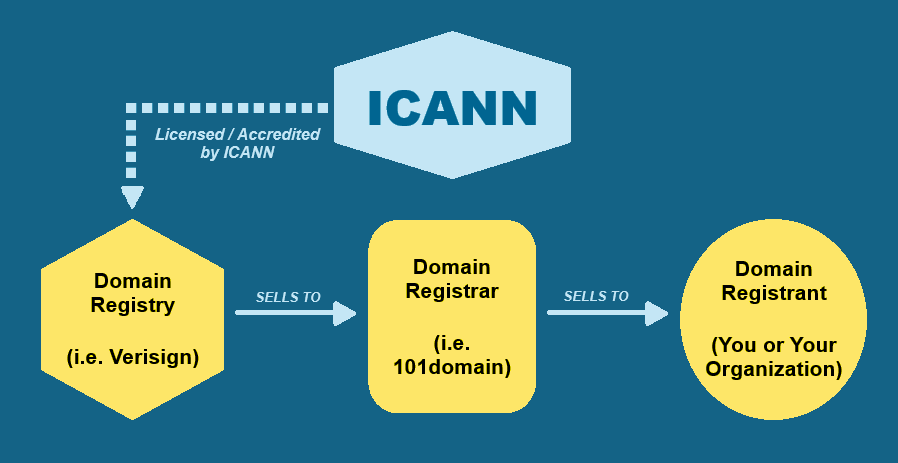
The Registry
The Registry is the organization that operates a generic specific top-level domain (gTLD), such as .COM, .ORG, or country-code TLDs (ccTLD) like .IE (Ireland).
Responsibilities:
-
Maintains the master database of all domain names under its TLD.
-
Sets rules, pricing, and registration policies for its TLD.
-
Works with registrars to make domain names available to the public.
Example:
Verisign is the registry for the .com TLD.
For more details on the difference between gTLDs and ccTLDs, see our articles on What is a gTLD? and What is a ccTLD?.
The Registrar
A Registrar is a company accredited by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) to sell a domain to the public, like 101domain..
Responsibilities:
-
Acts as the middleman between registrants and registries.
-
Registers domain names for individuals and businesses.
-
Provides a control panel for managing domain settings (contact info, DNS records, etc.).
-
Handles payments for domain registration and renewal.
-
Example:
101domain is a registrar.
The Registrant
The Registrant is the individual or organization that registers and owns the rights to use a domain name.
Responsibilities:
-
Purchases a domain name through a registrar.
-
Maintains accurate contact information (often listed in the public domain contact database unless privacy protection is used).
-
Renews the domain to keep ownership.
-
Example:
If you register mydomain.com, you are the registrant.
Summary
Registries like Verisign operate top-level domains, while registrars such as 101domain sell and manage them for registrants, who are the individuals or organizations that own the domain names.
|
Role |
What They Do |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Registry |
Operates TLD, maintains database, sets rules |
Verisign (.com) |
|
Registrar |
Sells domains, manages registration, supports users |
101domain |
|
Registrant |
Registers and owns domain, maintains info |
You/Your Org |
If you have any questions and want to learn more about the differences, please contact our friendly Support Team at 877.983.6624 (United States) or +1.760.444.8674 (International).